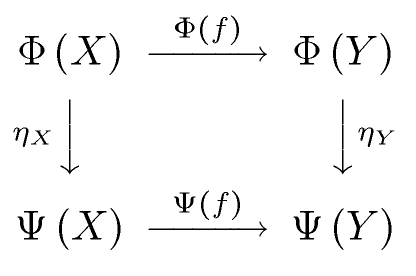Category theory/Natural transformation
map even $ maybeToList $ Just 5
yields the same as
maybeToList $ fmap even $ Just 5
yields: both yield
[False]
In the followings, this example will be used to illustrate the notion of natural transformation. If the examples are exaggerated and/or the definitions are incomprehensible, try #External links.
Definition
- Let , denote categories.
- Let be functors.
- Let . Let .
Let us define the natural transformation. It associates to each object of a morphism of in the following way (usually, not sets are discussed here, but proper classes, so I do not use term “function” for this mapping):
- . We call the component of at A.
Thus, the following diagram commutes (in ):
Example: maybeToList
maybeToListAs already mentioned
map even $ maybeToList $ Just 5
yields the same as
maybeToList $ fmap even $ Just 5
yields: both yield
[False]
This example will be shown in the light of the above definition in the followings.
Vertical arrows: sides of objects
… showing how the natural transformation works.
maybeToList :: Maybe a -> [a]
Left: side of X object
maybeToList :: Maybe Int -> [Int]
| |
Nothing
|
[]
|
Just 0
|
[0]
|
Just 1
|
[1]
|
Right: side of Y object
maybeToList :: Maybe Bool -> [Bool]
| |
Nothing
|
[]
|
Just True
|
[True]
|
Just False
|
[False]
|
Horizontal arrows: sides of functors
even :: Int -> Bool
Side of functor
fmap even:: Maybe Int -> Maybe Bool
| |
Nothing
|
Nothing
|
Just 0
|
Just True
|
Just 1
|
Just False
|
Side of functor
map even:: [Int] -> [Bool]
| |
[]
|
[]
|
[0]
|
[True]
|
[1]
|
[False]
|
Commutativity of the diagram
both paths span between
Maybe Int -> [Bool]
| ||
map even . maybeToList
|
maybeToList . fmap even
| |
Nothing
|
[]
|
[]
|
Just 0
|
[True]
|
[True]
|
Just 1
|
[False]
|
[False]
|
Remarks
evenhas a more general type (Integral a => a -> Bool) than described here- Words “side”, “horizontal”, “vertical”, “left”, “right” serve here only to point to the discussed parts of a diagram, thus, they are not part of the scientific terminology.
- If You want to modify the commutative diagram, see its source code (in LaTeX using
amscd).
Operations
Mixed
The “mixed” operations described below will be important also in understanding the definition of “monad” concept in category theory.
Functor and natural transformation
Let us imagine a parser library, which contains functions for parsing a form. There are two kinds of cells:
- containing data which are optional (e.g. name of spouse)
- containing data which consist of an enumeration of items (e.g. names of acquired languages)
spouse :: Parser (Maybe String)
languages :: Parser [String]
Let us imagine we have any processing (storing, archiving etc.) function which processes lists (or any other reason which forces us to convert our results to list format and exclude any Maybe's). (Perhaps, all this example is impractical and exaggerated, because in real life we should solve the whole thing in other ways.)
Thus, we want to build a parser combinator (we could notate it graphically with something like ) which converts a “zero-ore-one-occurrence” like parser to a “zero-or-one-or-many-occurrences” like parser.
We can convert Maybe to list with maybeToList
But if we want to do something similar with a parser on Maybe's to achieve a parser on list, then maybeToList is not enough alone, we must fmap it.
E.g. if we want to convert a parser like spouse to be of the same type as languages:
fmap maybeToList spouse
Let us see the types: We start with
spouse :: Parser (Maybe String)
or using notion of composing functors
We want to achieve
fmap maybeToList spouse :: Parser [String]
thus we can infer
fmap maybeToList :: Parser (Maybe [String]) -> Parser [String]
In fact, we have a new “datatype converter”: converting not Maybe's to lists, but parser on Maybe to Parser on list. Let us notate the corresponding natural transformation with :
- To each we associate
Summary:
- Let be categories
- functors
- functor
- natural transformation
Then let us define a new natural transformation:
Natural transformation and functor
- Let be categories
- functor
- functors
- natural transformation
Then let us define a new natural transformation:
It can be illustrated by Haskell examples, too. Understanding it is made harder (easier?) by the fact that Haskell's type inference “(dis)solves” the main point, thus there is no “materialized” manifestation of it.
convert :: Maybe (Term a) -> [Term a]
Unlike seen at , the definition of this converter will not show much novelty:
convert = maybeToList
the most interesting thing is done automatically by type inference.
External links
- The corresponding HaWiki article is not migrated here yet, so You can see it for more information.
- Wikipedia's Natural transformation article
- Toposes, Triples and Theories written by Michael Barr and Charles Wells.