TerraHS: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[Image:Logo terrahs.png]] is a software component that enables the development of geographical applications in a functional language, using the data handling capabilities of [http://www.terralib.org/ TerraLib]. TerraLib is a C++ library that supports different spatial database management systems, and that includes a large number of spatial algorithms. As a result, we get a combination of the good features of both programming paradigms. | [[Image:Logo terrahs.png]] is a software component that enables the development of geographical applications in a functional language, using the data handling capabilities of [http://www.terralib.org/ TerraLib]. TerraLib is a C++ library that supports different spatial database management systems, and that includes a large number of spatial algorithms. As a result, we get a combination of the good features of both programming paradigms. | ||
[[How to use Haskell for GIS]] | |||
== Features == | == Features == | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 25 November 2009
What is it ?
 is a software component that enables the development of geographical applications in a functional language, using the data handling capabilities of TerraLib. TerraLib is a C++ library that supports different spatial database management systems, and that includes a large number of spatial algorithms. As a result, we get a combination of the good features of both programming paradigms.
is a software component that enables the development of geographical applications in a functional language, using the data handling capabilities of TerraLib. TerraLib is a C++ library that supports different spatial database management systems, and that includes a large number of spatial algorithms. As a result, we get a combination of the good features of both programming paradigms.
Features
The major features are:
- Input and output formats: Layers or themes from TerraLib databases (just MySQL), Esri Shape File (*.shp), TIFF file.
- Data types: Raster or image (just 8 bits), Vectors (Point, Line, Polygon and Cell), Temporal (DateTime, Interval)
- Topological operators: intersects, within, touches, crosses ...
- Geometric operations: intersection, union, difference, rotation.
- Metrical operations: perimeter, area, distance, centroid, shapeindex, compacity, fractal
Demos
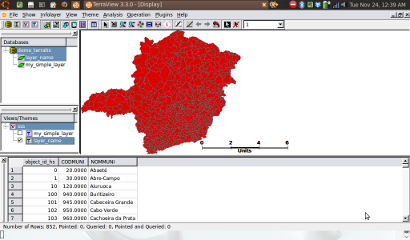
The following figure is one example of a vector data can be exported to a TerraLib database, and then it can be visualized with TerraView.
The pattern for a main program in TerraHS has the folowing structure:
module Main(main) where
import TerraHS
host = "localhost";
dbname = "demo_terrahs";
user = "root";
password = "root";
main:: IO()
main = do
-- loading a vector data from a shape file
gos <- loadVectorFile "MG_MUN96.shp"
-- open a connection
db <- open (TeMySQL host user password dbname)
-- saving in a database layer
store db "layer_name" gos
print "saved"Two different outcomes from a image data and theirs respective operations (a)input image, (b) inverted image and (c) reverse image.
The following examples use this data:
- Opening and saving shape file
- Opening a shape file and saving in database
- Opening and save tiff image files
- Simple spatial operations demo
- Understanding how to create a geoobject data type
- Opening a raster data from database
- Opening a tiff file and saving in database
- Loading geoobjects from a database and saving a shape file
Its possible to run in the ghci:
#ghci SpatialOper.hs
printing some test values, e.g.:
Main> main Loading package syb ... linking ... done. Loading package base-3.0.3.0 ... linking ... done. Loading package terrahs-0.8 ... linking ... done. TePoint (12.5,10.0) TeLine2D [(1.0,1.0),(1.0,2.0),(1.0,7.0)] TePolygon [TeLine2D [(1.0,1.0),(1.0,2.0),(3.0,2.0),(3.0,1.0),(1.0,1.0)]] False True False 2.0
or compile and run:
#ghc SpatialOper.hs -package terrahs-0.8 -o main #main
More details about the api in source documentation - online (HTML)
Download and Installation
TerraHS is available in cabal package from Hackage. See How to install a Cabal package in Linux or Windows.
Installation notes for Linux
Software dependencies in debian package
The installation procedure:
#sudo dpkg -i package.deb
The uninstallation procedure:
#sudo dpkg -r package
Software dependencies in source file
The installation procedure:
#tar xvzf package.tar.gz #cd package #./configure #make #sudo make install
The uninstallation procedure:
#cd package #sudo make uninstall
Installation notes for Windows
Coming soon
Software dependencies
TerraHS is a Haskell GIS application built using the TerraLib GIS library. In below, is available a debian packages for TerraLib. TerraHS-0.8 uses the TerraLib-3.3.0 version.
![]() TerraLib-3.3.0 for (Ubuntu 9.04 (x86))
TerraLib-3.3.0 for (Ubuntu 9.04 (x86))
Optional, but is recommended to install the TerraView application.TerraView is a GIS application based on TerraLib, a GIS library to handle vector and raster data in geographical DBMS such as Access, PostgreSQL, MySQL and Oracle Spatial.
![]() TerraView-3.3.0 for (Ubuntu 9.04 (x86))
TerraView-3.3.0 for (Ubuntu 9.04 (x86))
The TerraLib and TerraView source files can be downloaded from official sites:
We have developed some specific libraries to support some functionalities for TerraHS. The libraries can be installed from an unique package (TerraLib4c+Translib)
![]() TerraHSdependecies for Ubuntu 9.04 (x86)
TerraHSdependecies for Ubuntu 9.04 (x86)
Or can be download in separated way:
Translib, a library for translation among different geographic format files (no database connection), based in the TerraLib library. This library is required for TerraHS to deal whith shape files (*.shp).
Terralib4c, a library that maps c++ Terralib functions and classes to C functions. Required by Haskell to do binding with TerraLib api.
Papers, thesis and Reports
Some papers and thesis that use TerraHS:
- Sérgio Costa, Gilberto Câmara, et.al. Prototyping GIS Application in Functional Programming. In: GeoPantanal, 2009, Corumbá. Anais do II Geopantanal, 2009. download
- Costa, S. S., Câmara, G., & Palomo, D. (2007). TerraHS: Integration of Functional Programming and Spatial Databases for GIS Application Development. (pp. 127-149). Advances in Geoinformatics. Springer. link
- Sergio Costa, Gilberto Câmara, Danilo Palomo. TerraHS: Integration of Functional Programming and Spatial Databases for GIS Application Development. VIII Brazilian Symposium in Geoinformatics, GeoInfo 2006, Campos do Jordão, 2006. download
- Olga Bittencourt, Gilberto Câmara, Lúbia Vinhas, Joice Mota. Rule-based Evolution of Typed Spatio-temporal Objects. IX Brazilian Symposium in Geoinformatics, GeoInfo 2007, Campos do Jordão, 2007.download
- Sérgio Rosim. Estrutura baseada em grafos para representação unificada de fluxos locais para modelagem hidrológica distribuída. PhD Thesis in Computer Science at INPE, 2008.download