OpenGLTutorial1
This tutorial [1] was originally written by Mikael Vejdemo Johansson, and was copied here with permission.
After having failed following the googled tutorial in HOpenGL programming, I thought I'd write down the steps I actually can get to work in a tutorial-like fashion. It may be a good idea to read this in parallell to the tutorial linked, since Panitz actually brings a lot of good explanations, even though his syntax isn't up to speed with the latest HOpenGL at all points.
Note: GHCI interactive shell has problems running these program on some platforms (such as Mac OS X). Vompile these programs with ghc, and run the generated executables.
Hello World
First of all, we'll want to load the OpenGL libraries, throw up a window, and generally get to grips with what needs to be done to get a program running at all.
import Graphics.Rendering.OpenGL
import Graphics.UI.GLUT
main :: IO ()
main = do
(progname, _) <- getArgsAndInitialize
createWindow "Hello World"
displayCallback $= flush
mainLoopThis code throws up a window, with a given title, and sets the main display function to do nothing but flush the (empty) graphics buffer. This is the skeleton that we'll be building on to.
Save it to HelloWorld.hs and compile it by running ghc -package GLUT HelloWorld.hs -o HelloWorld.
You will see a window open, with the title "Hello World", with either a blank canvas, or with some garbage graphics content pulled from somewhere in your system's graphics memory.
In either case, this program is profoundly worthless.
At a minimum, let's have our program display a clean blank canvas:
So we modify our code to the following:
import Graphics.Rendering.OpenGL
import Graphics.UI.GLUT
main :: IO ()
main = do
(progname, _) <- getArgsAndInitialize
createWindow "Hello World"
displayCallback $= display
mainLoop
display :: IO ()
display = do
clear [ ColorBuffer ]; flushThis defines a function "display" that calls a few OpenGL functions: "clear" to clear out the graphics color state (so we get a blank canvas), and "flush" to push our OpenGL commands down to the system graphics for actual display.
We don't call "display" directly. (In fact, we don't call any graphics drawing functions directly). Instead, we set a display callback, and then call mainLoop. In mainLoop, OpenGL akes over, handles all the details of interacting with the OS and refreshing our window, calling our displayCallback to draw graphics.
displayCallback is a Data.IORef (mutable state variable), which we set using a call to ($=).
Save this to the HelloWorld.hs, recompile, and rerun. This program displays an endless series of blank canvases (a solid blank image).
The displayCallback is a globally defined IORef, which can be accessed through a host of functions defined in Data.IORef. In OpenGL StateVar module, there is a HasSetter type class and an IORef implementation providing functions ($=) (assignment) and get to fascilitate interactions with these state variables.
height = newIORef 1.0
currentheight <- get height
height $= 1.5Using the drawing canvas
So, we have a window, we have a display callback that clears the canvas. Don't we want more out of it? Sure we do. So let's draw some things.
import Graphics.Rendering.OpenGL
import Graphics.UI.GLUT
myPoints :: [(GLfloat,GLfloat,GLfloat)]
myPoints = map (\k -> (sin(2*pi*k/12),cos(2*pi*k/12),0.0)) [1..12]
main = do
(progname, _) <- getArgsAndInitialize
createWindow "Hello World"
displayCallback $= display
mainLoop
display = do
clear [ColorBuffer]
renderPrimitive Points $ mapM_ (\(x, y, z)->vertex$Vertex3 x y z) myPoints
flushNow, the important thing to notice in this code extract is that last line. It starts a rendering definition, gives the type to be rendered, and then a sequence of function calls, each of which adds a vertex to the rendering canvas. The statement is basically equivalent to something along the lines of
renderPrimitive Points do
vertex Vertex3 ...
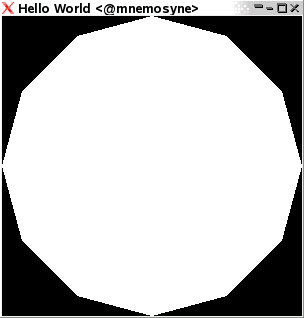
vertex Vertex3 ...for appropriate triples of coordinate values at the appropriate places. This results in the rendition here:
We can replace Points with other primitives, leading to the rendering of:
Triangles
Each three coordinates following each other define a triangle. The last n mod 3 coordinates are ignored.
Keyword Triangles
Triangle strips
Triangles are drawn according to a “moving window” of size three, so the two last coordinates in the previous triangle become the two first in the next triangle.
Keyword TriangleStrip
Triangle fans
Triangle fans have the first given coordinate as a basepoint, and takes each pair of subsequent coordinates to define a triangle together with the first coordinate.
Keyword TriangleFan
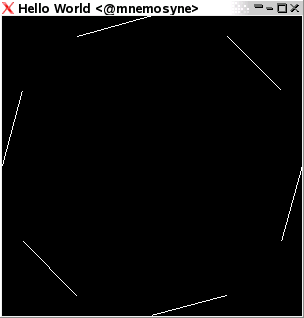
Lines
Each pair of coordinates define a line.
Keyword Lines
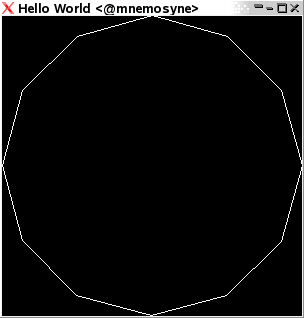
Line loops
With line loops, each further coordinate defines a line together with the last coordinate used. Once all coordinates are used up, an additional line is drawn back to the beginning.
Keyword LineLoop
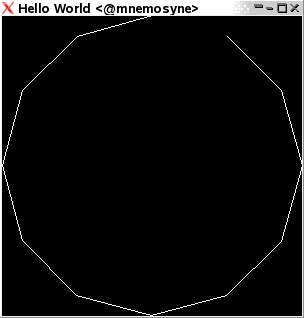
Line strips
Line strips are like line loops, only without the last link added.
Keyword LineStrip
Quadrangles
For the Quads keyword, each four coordinates given define a quadrangle.
Keyword Quads
Quadrangle strips
And a Quadstrip works as the trianglestrip, only the window is 4 coordinates wide and steps 2 steps each time, so each new pair of coordinates attaches a new quadrangle to the last edge of the last quadrangle.
Keyword QuadStrip
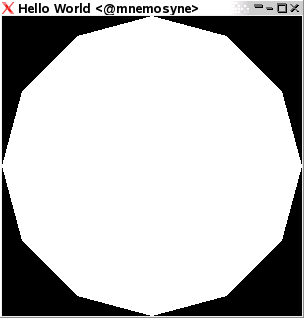
Polygon
A Polygon is a filled line loop. Simple as that!
Keyword Polygon
There are more things we can do on our canvas than just spreading out coordinates. Within the command list constructed after a renderPrimitive, we can give several different commands that control what things are supposed to look like, so for instance we could use the following:
display = do
clear [ColorBuffer]
renderPrimitive Quads $ do
color $ (Color3 (1.0::GLfloat) 0 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) 0 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) 0.2 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0.2::GLfloat) 0.2 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0.2::GLfloat) 0 0)
color $ (Color3 (0::GLfloat) 1 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) 0 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) (-0.2) 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0.2::GLfloat) (-0.2) 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0.2::GLfloat) 0 0)
color $ (Color3 (0::GLfloat) 0 1)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) 0 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) (-0.2) 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 ((-0.2)::GLfloat) (-0.2) 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 ((-0.2)::GLfloat) 0 0)
color $ (Color3 (1::GLfloat) 0 1)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) 0 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 (0::GLfloat) 0.2 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 ((-0.2::GLfloat)) 0.2 0)
vertex $ (Vertex3 ((-0.2::GLfloat)) 0 0)
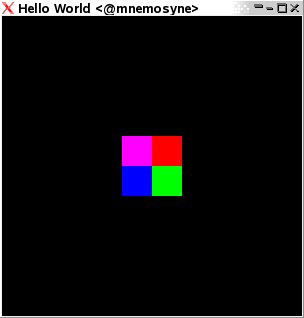
flushin order to produce these four coloured squares:
where each color command sets the color for the next item drawn, and the vertex commands give vertices for the four squares.
Callbacks - how we react to changes
We have already seen one callback in action: displayCallBack. The Callbacks are state variables of the HOpenGL system, and are called in order to handle various things that may happen to the place the drawing canvas lives. For a first exercise, go resize the latest window you've used. Go on, do it now.
I bet it looked ugly, didn't it?
This is because we have no code handling what to do if the window should suddenly change. Handling this is done in a callback, residing in the IORef reshapeCallback. Similarily, repainting is done in displayCallback, keyboard and mouse input is in keyboardMouseCallback, and so on. We can refer to the HOpenGL documentation for window callbacks and for global callbacks. Window callbacks are things like display, keyboard and mouse, and reshape. Global callbacks deal with timing issues (for those snazzy animations) and the menu interface systems.
In order for a callback to possibly not be defined, most are typed within the Maybe monad, so by setting the state variable to Nothing, a callback can be disabled. Thus, setting callbacks is done using the keyword Just. We'll add a callback for reshaping the window to our neat code, changing the main function to:
main = do
(progname, _) <- getArgsAndInitialize
createWindow "Hello World"
displayCallback $= display
reshapeCallback $= Just reshape
mainLoop
reshape s@(Size w h) = do
viewport $= (Position 0 0, s)
postRedisplay NothingHere, the code for the reshape function resizes the viewport so that our drawing area contains the entire new window. After setting the new viewport, it also tells the windowing system that something has happened to the window, and that therefore, the display function should be called.
Summary
So, in conclusion, so far we can display a window, post basic callbacks to get the windowhandling to run smoothly, and draw in our window. Next installment of the tutorial will bring you 3d drawing, keyboard and mouse interactions, the incredible power of matrices and the ability to rotate 3d objects for your leisure. Possibly, we'll even look into animations.