Difference between revisions of "FieldTrip"
m (→Abstract) |
(fixed doc pointer and example details) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[Image:Torus-pair-d-shadowed.png|right|thumb|300px|Torus pair modeled and rendered in FieldTrip]] |
[[Image:Torus-pair-d-shadowed.png|right|thumb|300px|Torus pair modeled and rendered in FieldTrip]] |
||
| − | '''FieldTrip''' is a library for functional 3D graphics, intended for building static, animated, and interactive 3D geometry, efficient |
+ | '''FieldTrip''' is a library for functional 3D graphics, intended for building static, animated, and interactive 3D geometry, efficient |
| + | enough for real-time synthesis and display. |
||
Our first renderer uses OpenGL, with the usual visual limitations. |
Our first renderer uses OpenGL, with the usual visual limitations. |
||
Since FieldTrip is functional, it is about ''being'' rather than ''doing''. |
Since FieldTrip is functional, it is about ''being'' rather than ''doing''. |
||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
Besides this wiki page, here are more ways to find out about and get involved with FieldTrip: |
Besides this wiki page, here are more ways to find out about and get involved with FieldTrip: |
||
* Join the [http://www.haskell.org/mailman/listinfo/FieldTrip FieldTrip mailing list]. |
* Join the [http://www.haskell.org/mailman/listinfo/FieldTrip FieldTrip mailing list]. |
||
| − | * Visit the [http://hackage.haskell.org/cgi-bin/hackage-scripts/package/FieldTrip Hackage page] for library documentation and to download |
+ | * Visit the [http://hackage.haskell.org/cgi-bin/hackage-scripts/package/FieldTrip Hackage page] for library documentation and to download |
| + | & install. |
||
* Or install with <tt>cabal install FieldTrip</tt>. See [[#Installation dependencies|Installation dependencies]] below. |
* Or install with <tt>cabal install FieldTrip</tt>. See [[#Installation dependencies|Installation dependencies]] below. |
||
* Get the code repository: <tt>darcs get http://code.haskell.org/FieldTrip</tt>. |
* Get the code repository: <tt>darcs get http://code.haskell.org/FieldTrip</tt>. |
||
| Line 24: | Line 26: | ||
== Basic types == |
== Basic types == |
||
| − | The basic purpose of the core FieldTrip library is to allow a user build 3D geometry, from individual simple shapes to full 3D scenes. |
+ | The basic purpose of the core FieldTrip library is to allow a user build 3D geometry, from individual simple shapes to full 3D scenes. |
| + | The principal types are as follows. |
||
; <hask>Geometry3</hask> |
; <hask>Geometry3</hask> |
||
| Line 30: | Line 33: | ||
; <hask>Surf a = (a,a) -> (a,a,a)</hask> |
; <hask>Surf a = (a,a) -> (a,a,a)</hask> |
||
| − | : Parametric surfaces, i.e., mappings from 2D to 3D. Normals are constructed automatically and exactly via derivatives, thanks to the |
+ | : Parametric surfaces, i.e., mappings from 2D to 3D. Normals are constructed automatically and exactly via derivatives, thanks to the |
| + | [[vector-space]] library. These normals are used for shading. For simplicity and composability, ''surfaces are curved'', not faceted. |
||
| + | Surface ''rendering'' tessellates adaptively, caching tessellations in an efficient, infinite data structure for reuse. The mechanism |
||
| + | for choosing tessellation is a very primitive placeholder. FieldTrip provides some basic shapes of surfaces (spheres, torus, cubes, etc) |
||
| + | and many functions for manipulating surfaces, colors, etc. |
||
; <hask>Geometry2</hask> |
; <hask>Geometry2</hask> |
||
| Line 36: | Line 43: | ||
; <hask>Image o = (R,R) -> o</hask> |
; <hask>Image o = (R,R) -> o</hask> |
||
| − | : A primitive placeholder for functional imagery in the spirit of [http://conal.net/Pan Pan]. The intention is to use this type or |
+ | : A primitive placeholder for functional imagery in the spirit of [http://conal.net/Pan Pan]. The intention is to use this type or |
| + | something like it for texture mapping. Much design and implementation work to be done. |
||
== Example == |
== Example == |
||
| Line 47: | Line 55: | ||
tor = torus 1 (2/5) |
tor = torus 1 (2/5) |
||
f :: Col -> R -> Geometry3 |
f :: Col -> R -> Geometry3 |
||
| − | f col dx = |
+ | f col dx = materialG (plastic col) (move3X dx tor) |
</haskell> |
</haskell> |
||
| − | where <hask>pivot3X</hask> and <hask>move3X</hask> are simple helper functions for 3D transformation, and <hask>plasmat</hask> applies a |
+ | where <hask>pivot3X</hask> and <hask>move3X</hask> are simple helper functions for 3D transformation, and <hask>plasmat</hask> applies a |
| + | color with a plastic look (defined in <code>Test.hs</code>). |
||
| − | The <code>[http:// |
+ | The <code>[http://hackage.haskell.org/packages/archive/FieldTrip/0.2.2/doc/html/Graphics-FieldTrip-Geometry3.html#v%3Atorus torus]</code> function used here is a |
| + | simple wrapper around a parametric surface defined as follows: |
||
<haskell> |
<haskell> |
||
-- | Torus, given radius of sweep circle and cross section |
-- | Torus, given radius of sweep circle and cross section |
||
| Line 57: | Line 67: | ||
torus sr cr = revolve (const (sr,0) ^+^ cr *^ circle) |
torus sr cr = revolve (const (sr,0) ^+^ cr *^ circle) |
||
</haskell> |
</haskell> |
||
| − | where <hask>revolve</hask> and <hask>circle</hask> are defined in |
+ | where <hask>revolve</hask> and <hask>circle</hask> are defined in |
| + | [http://hackage.haskell.org/packages/archive/FieldTrip/latest/doc/html/Graphics-FieldTrip-ParamSurf.html Graphics.FieldTrip.ParamSurf], along with other tools for shape generation. |
||
| − | The trick to turning this polymorphic <hask>torus</hask> function into a <hask>Geometry3</hask> is to use a derivative tower (from |
+ | The trick to turning this polymorphic <hask>torus</hask> function into a <hask>Geometry3</hask> is to use a derivative tower (from |
| + | [[vector-space]]) for the type parameter <hask>s</hask>. |
||
<haskell> |
<haskell> |
||
surfG :: Surf (Vector2 R :> R) -> Geometry3 |
surfG :: Surf (Vector2 R :> R) -> Geometry3 |
||
| Line 71: | Line 83: | ||
== FieldTrip meets Reactive == |
== FieldTrip meets Reactive == |
||
| − | FieldTrip contains no support for animation, because we intend it to be used with the [[Reactive]] functional reactive programming |
+ | FieldTrip contains no support for animation, because we intend it to be used with the [[Reactive]] functional reactive programming |
| + | ([[FRP]]) library (and possibly other animation frameworks). |
||
By design, FieldTrip is completely orthogonal to any formulation or implementation of FRP. |
By design, FieldTrip is completely orthogonal to any formulation or implementation of FRP. |
||
| Line 93: | Line 106: | ||
Then run the example: |
Then run the example: |
||
<pre> |
<pre> |
||
| − | *Test> anim3 (spinningG torusPair) |
+ | *Test> anim3 (const (spinningG torusPair)) |
Loading package OpenGL-2.2.1.1 ... linking ... done. |
Loading package OpenGL-2.2.1.1 ... linking ... done. |
||
Loading package syb ... linking ... done. |
Loading package syb ... linking ... done. |
||
| Line 130: | Line 143: | ||
</haskell> |
</haskell> |
||
| − | That line allows a graceful exit, e.g., back into ghci. However, it relies on freeglut. If you have (non-free) GLUT, comment it out. |
+ | That line allows a graceful exit, e.g., back into ghci. However, it relies on freeglut. If you have (non-free) GLUT, comment it out. |
| + | I'd like to make the check at runtime, but I don't know how. Help, please. |
||
Revision as of 01:56, 19 November 2008
Abstract
FieldTrip is a library for functional 3D graphics, intended for building static, animated, and interactive 3D geometry, efficient enough for real-time synthesis and display. Our first renderer uses OpenGL, with the usual visual limitations. Since FieldTrip is functional, it is about being rather than doing. One describes what models are, not how to render them.
FieldTrip is work-in-progress. It's being released to show what's going on and see who's interested in collaborating on developing it further.
Besides this wiki page, here are more ways to find out about and get involved with FieldTrip:
- Join the FieldTrip mailing list.
- Visit the Hackage page for library documentation and to download
& install.
- Or install with cabal install FieldTrip. See Installation dependencies below.
- Get the code repository: darcs get http://code.haskell.org/FieldTrip.
- Report bugs and request features on the tracker.
Basic types
The basic purpose of the core FieldTrip library is to allow a user build 3D geometry, from individual simple shapes to full 3D scenes. The principal types are as follows.
Geometry3- 3D geometry. These values can be spatially transformed in space (affinely: scale, rotate, translate) and combined (union).
Surf a = (a,a) -> (a,a,a)- Parametric surfaces, i.e., mappings from 2D to 3D. Normals are constructed automatically and exactly via derivatives, thanks to the
vector-space library. These normals are used for shading. For simplicity and composability, surfaces are curved, not faceted. Surface rendering tessellates adaptively, caching tessellations in an efficient, infinite data structure for reuse. The mechanism for choosing tessellation is a very primitive placeholder. FieldTrip provides some basic shapes of surfaces (spheres, torus, cubes, etc) and many functions for manipulating surfaces, colors, etc.
Geometry2- 2D geometry. There's a function (
flatG) to embed 2D into 3D.
Image o = (R,R) -> o- A primitive placeholder for functional imagery in the spirit of Pan. The intention is to use this type or
something like it for texture mapping. Much design and implementation work to be done.
Example
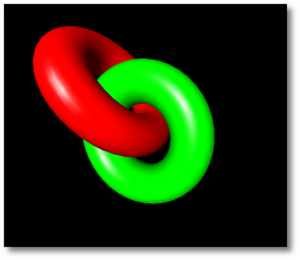
The code for the static torus pair shown above:
torusPair :: Geometry3
torusPair = f red (1/2) `mappend` pivot3X (f green (-1/2))
where
tor = torus 1 (2/5)
f :: Col -> R -> Geometry3
f col dx = materialG (plastic col) (move3X dx tor)
where pivot3X and move3X are simple helper functions for 3D transformation, and plasmat applies a
color with a plastic look (defined in Test.hs).
The torus function used here is a
simple wrapper around a parametric surface defined as follows:
-- | Torus, given radius of sweep circle and cross section
torus :: (Floating s, VectorSpace s, Scalar s ~ s) => s -> s -> Surf s
torus sr cr = revolve (const (sr,0) ^+^ cr *^ circle)
where revolve and circle are defined in
Graphics.FieldTrip.ParamSurf, along with other tools for shape generation.
The trick to turning this polymorphic torus function into a Geometry3 is to use a derivative tower (from
vector-space) for the type parameter s.
surfG :: Surf (Vector2 R :> R) -> Geometry3
torus :: R -> R -> Geometry3
torus sr cr = surfG (P.torus (pureD sr) (pureD cr))
[fill in more examples]
FieldTrip meets Reactive
FieldTrip contains no support for animation, because we intend it to be used with the Reactive functional reactive programming (FRP) library (and possibly other animation frameworks). By design, FieldTrip is completely orthogonal to any formulation or implementation of FRP.
The reactive-fieldtrip project connects Reactive and FieldTrip.
The picture above comes from an animation in reactive-fieldtrip.
Load src/Test.hs, as follows:
~/Haskell$ cd reactive-fieldtrip/src
~/Haskell/reactive-fieldtrip/src$ ghci
GHCi, version 6.10.1: http://www.haskell.org/ghc/ :? for help
Loading package ghc-prim ... linking ... done.
Loading package integer ... linking ... done.
Loading package base ... linking ... done.
Prelude> :l Test
:l Test
[1 of 2] Compiling FRP.Reactive.FieldTrip.Adapter ( FRP/Reactive/FieldTrip/Adapter.hs, interpreted )
[2 of 2] Compiling Test ( Test.hs, interpreted )
Ok, modules loaded: FRP.Reactive.FieldTrip.Adapter, Test.
Then run the example:
*Test> anim3 (const (spinningG torusPair))
Loading package OpenGL-2.2.1.1 ... linking ... done.
Loading package syb ... linking ... done.
Loading package base-3.0.3.0 ... linking ... done.
[...]
Loading package reactive-0.9.0 ... linking ... done.
Loading package FieldTrip-0.2.2 ... linking ... done.
Loading package reactive-glut-0.0.5 ... linking ... done.
Some videos
Problems and solutions
Installation dependencies
You may also need to install libghc6-opengl-dev and libghc6-glut-dev using synaptic or apt-get.
- To do: describe the symptoms that indicate when this extra installation is needed
GLUT and freeglut
You may encounter the following message when using reactive-glut or reactive-fieldtrip and freeglut:
user error (unknown GLUT call glutSetOption, check for freeglut)
The problem is the following line of code in FRP.Reactive.GLUT.SimpleGL in the reactive-glut package.
actionOnWindowClose $= MainLoopReturns
That line allows a graceful exit, e.g., back into ghci. However, it relies on freeglut. If you have (non-free) GLUT, comment it out. I'd like to make the check at runtime, but I don't know how. Help, please.