Search results
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- ..."parse tree for Haskell" is likely to be a concrete data type, whereas a "tree" data type is a corresponding [[Abstract data type]]. ...nteger</hask>, <hask>Bool</hask>, <hask>[(String,String)]</hask> and <hask>Tree String</hask> are concrete data types.864 bytes (135 words) - 22:06, 20 December 2006
- ...e difficult than insertion. His solution is to use a concrete view of the tree which simplifies the operation, and as a result, comes up with a new repres Here is a simple binary search tree type:5 KB (845 words) - 02:22, 4 January 2008
- ...order/2 that construct the preorder and inorder sequence of a given binary tree, respectively. The results should be atoms, e.g. 'abdecfg' for the preorder ...verse direction; i.e. given a preorder sequence, construct a corresponding tree? If not, make the necessary arrangements.2 KB (280 words) - 03:43, 10 January 2017
- ...ing some kind of binary tree, typically a size balanced tree or a Patricia tree. While binary trees provide good asymptotic performance, their real world p876 bytes (134 words) - 13:45, 17 December 2012
- import Tree (Tree (Leaf, Branch)) type CL = Tree BaseSymbol689 bytes (98 words) - 14:34, 4 August 2006
- (**) Lisp-like tree representation. The following pictures show how multiway tree structures are represented in Lisp.2 KB (276 words) - 03:52, 10 January 2017
- data Tree = Nil | Node !Int Tree Tree -- stretch memory tree7 KB (1,253 words) - 22:33, 22 February 2011
- -- get currently selected node in the tree tree <- Model.treeViewGetSelection treeview3 KB (485 words) - 10:07, 7 June 2011
- (count, markov1, Tree, encode_huffman, decode_huffman) -- Build a Huffman tree...5 KB (730 words) - 01:59, 9 March 2007
- A node of a binary tree is at level N if the path from the root to the node has length N-1. The roo atLevel :: Tree a -> Int -> [a]741 bytes (125 words) - 13:40, 25 December 2016
- Collect the internal nodes of a binary tree in a list An internal node of a binary tree has either one or two non-empty successors. Write a predicate internals/2 t717 bytes (98 words) - 13:39, 25 December 2016
- ...y subtree (nil) is encountered during the tree traversal. For example, the tree shown in problem P67 is represented as 'abd..e..c.fg...'. First, try to est data Tree a = Empty | Branch a (Tree a) (Tree a) deriving (Show, Eq)3 KB (285 words) - 03:44, 10 January 2017
File:Tree-like folding.gif Tree-like folding in composites production.(733 × 433 (5 KB)) - 14:00, 14 February 2013
File:WxGeneric MyTree.png WxGeneric example showing a tree structure(810 × 604 (31 KB)) - 12:46, 8 May 2009- ...is symmetric. Hint: Write a predicate mirror/2 first to check whether one tree is the mirror image of another. We are only interested in the structure, no ...nsider the cases where two immediate branches may not be the same, but the tree as a whole could be symmetric. Hence a mirror function is more encompassing1 KB (179 words) - 13:36, 25 December 2016
- ==Tree examples== Suppose we want to represent the following tree:3 KB (436 words) - 08:47, 22 May 2023
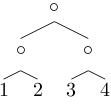
File:Tree-12-34.png Image for the ((1 2) (3 4)) tree(111 × 104 (2 KB)) - 11:28, 11 July 2007- [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abstract_syntax_tree Abstract syntax tree] at wikipedia.107 bytes (15 words) - 15:17, 6 February 2021
- -- returns a tree to a function that returns the sum of the numbered -- tree (see the Examples section for numberTree and sumTree) you may2 KB (379 words) - 03:00, 1 May 2009
- ...chapter 4 of the course, to write a predicate to construct a binary search tree from a list of integer numbers. add :: Ord a => a -> Tree a -> Tree a741 bytes (117 words) - 22:03, 23 April 2021