Tangible Value
Abstract
TV is a library for composing tangible values ("TVs"), i.e., values that carry along external interfaces. In particular, TVs can be composed to create new TVs, and they can be directly executed with a friendly GUI, a process that reads and writes character streams, or many other kinds interfaces. Values and interfaces are combined for direct use, and separable for composition. This combination makes for software that is ready to use and ready to reuse.
TV can be thought of as a simple functional formulation of the Model-View-Controller pattern. (My thanks to an anonymous ICFP referee for pointing out this connection.) The value part of a TV is the model, and the "interface" part, or "output" as it is called below, is the viewer. Outputs are built up compositionally from other outputs and from inputs (the controllers), as described below.
Besides this wiki page, here are more ways to learn about TV:
- Visit the Hackage page for library documentation.
- Install with cabal install TV.
As of version 0.2, I have moved the GUI functionality out of TV and into a small new package GuiTV. I moved it out to eliminate the dependency of core TV on Phooey and hence on wxHaskell, as the latter can be difficult to install. The GUI examples below require GuiTV.
GuiTV (better named "wxTV") is bit-rotten. There is also a very similar package to generate Gtk-based GUIs.
I'd love to hear your comments at the Talk:TV page.
First Example
Here is a tangible reverse function:
reverseT :: CTV (String -> String)
reverseT = tv (oTitle "reverse" defaultOut) reverseThe tv function combines an interface and a value. In this example, the interface is the default for string functions, wrapped with the title "reverse".
TV "interfaces" are more than just GUIs. Here are two different renderings of reverseT. (User input is shown in italics in the runIO version).
Running:
runUI reverseTrunIO reverseT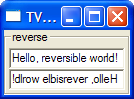
*Examples> runIO reverseT reverse: Hello, reversible world. .dlrow elbisrever ,olleH *Examples>
We'll see later that "runUI" and "runIO" are both type-specialized synonyms for a more general function.
Outputs
What I've been calling an "interface" is a value of type COutput a for a type a. For instance, for reverseT, a is String->String. The reason for the C prefix is explained below. At the heart of TV is a small algebra for constructing these outputs. Weve already seen one output function, oTitle. Another one is showOut, which is an output for all Show types. For instance,
total :: Show a => COutput a
total = oTitle "total" showOutInputs and function-valued outputs
Just as an output is a way to deliver (or consume) a value, an "input" is a way to obtain (or produce) a value. For example, here are two inputs, each specifying an initial value and a value range, and each given a title.
apples, bananas :: CInput Int
apples = iTitle "apples" defaultIn
bananas = iTitle "bananas" defaultInNow for the fun part. Let's combine the apples and bananas inputs and the total output to make a function-valued output.
shoppingO :: COutput (Int -> Int -> Int)
shoppingO = oTitle "shopping list" $
oLambda apples (oLambda bananas total)And a TV:
shopping :: CTV (Int -> Int -> Int)
shopping = tv shoppingO (+)Running:
runUI shoppingrunIO shopping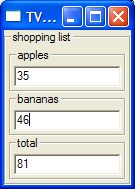
shopping list: apples: 8 bananas: 5 total: 13
A variation
Here is an uncurried variation:
shoppingPr :: CTV ((Int,Int) -> Int)
shoppingPr = tv ( oTitle "shopping list -- uncurried" $
oLambda (iPair apples bananas) total )
(uncurry (+))However, there's a much more elegant formulation, using uncurryA and $$ from DeepArrow:
shoppingPr = uncurryA $$ shoppingRunning:
runUI shoppingPrrunIO shoppingPr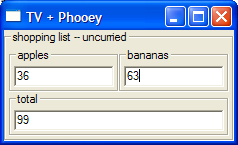
shopping list -- uncurried: apples: 8 bananas: 5 total: 13
The general story
TVs, outputs, and inputs are not restricted to GUIs and IO. In general, they are parameterized by the mechanics of "transmitting values", i.e., delivering ("sinking") output and gathering ("sourcing") input.
data Input src a
data Output src snk a
type TV src snk aThe "sources" will be applicative functors (AFs), and the "sinks" will be contravariant functors.
In the examples above, we've used two different mechanisms, namely Phooey's UI AF and IO. The sinks are counterparts IU and OI.
The functions runUI and runIO used in examples above are simply type-specialized synonyms for runTV
runUI :: TV UI IU a -> IO ()
runUI = runTV
runIO :: TV IO OI a -> IO ()
runIO = runTVCommon Ins and Outs
The examples reverseT and shoppingT above used not only the generic Output and Input operations, but also some operations that apply to AFs having a few methods for sourcing and sinking a few common types (strings, readables, showables, and booleans). The type constructors CInput, COutput, and CTV are universally quantified over sources and sinks having the required methods.
type CInput a = forall src.
(CommonIns src) => Input src a
type COutput a = forall src snk.
(CommonIns src, CommonOuts snk) => Output src snk a
type CTV a = forall src snk.
(CommonIns src, CommonOuts snk) => TV src snk aSorting examples
Here's a sorting TV (see interactLineRSrunUI:
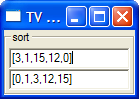
Note that sortT is polymorphic in value, and the type variable a as defaulted to Int. You could instead type-annotate its uses, e.g.,
runUI (sortT :: CTV ([String] -> [String]))
Composition of TVs
So far, we done a little composition of interfaces and combined them with values to construct TVs. Now let's look at composition of TVs.
First, wrap up the words and unwords functions:
wordsT :: CTV (String -> [String]) wordsT = tv ( oTitle "function: words" $ oLambda (iTitle "sentence in" defaultIn) (oTitle "words out" defaultOut)) words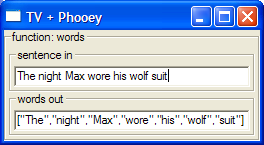
unwordsT :: CTV ([String] -> String) unwordsT = tv ( oTitle "function: unwords" $ oLambda (iTitle "words in" defaultIn) (oTitle "sentence out" defaultOut)) unwords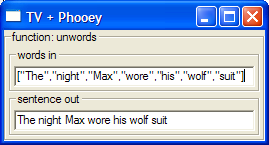
Finally, compose wordsT, unwordsT, and sortT
sortWordsT :: CTV (String -> String)
sortWordsT = wordsT ->| sortT ->| unwordsTRunning:
runUI sortWordsTrunIO sortWordsT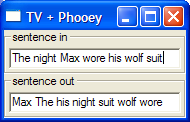
sentence in: The night Max wore his wolf suit sentence out: Max The his night suit wolf wore
The operator "->|
Transmission-specific interfaces
While some interfaces can be implemented for different means of transmission, others are more specialized.
GUIs
Here are inputs for our shopping example above that specifically work with Phooey's UI applicative functor.
applesU, bananasU :: Input UI Int
applesU = iTitle "apples" (islider 3 (0,10))
bananasU = iTitle "bananas" (islider 7 (0,10))
shoppingUO :: Output UI (Int -> Int -> Int)
shoppingUO = oTitle "shopping list" $ oLambda applesU (oLambda bananasU total)We can then make curried and uncurried TVs:
code runUI rendering tv shoppingUO (+)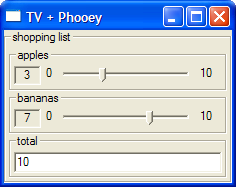
uncurryA $$ tv shoppingUO (+)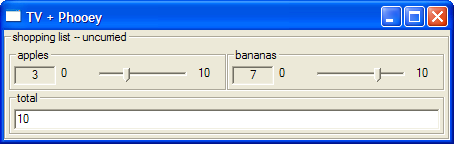
Note: We could define other type classes, besides CommonInsOuts. For instance, islider could be made a method of a GuiArrow class, allowing it to be rendered in different ways with different GUI toolkits or even using HTML and Javascript.
IO
We can use IO operations in TV interfaces. The corresponding sink is OI, defined in TypeCompose. TV provides a few functions in its IO moduleinteract function.
interactOut :: Output IO OI (String -> String)
interactOut = oLambda contentsIn stringOutAssuming we have a file "test.txt" containing some lines of text, we can use it to test string transformations.
testO :: Output IO OI (String -> String)
testO = oLambda (fileIn "test.txt") defaultOutFirst, let's define higher-order functions that apply another function to the lines or on the words of a string.
onLines, onWords :: ([String] -> [String]) -> (String -> String)
onLines f = unlines . f . lines
onWords f = unwords . f . wordsNext, specializations that operate on each line or word:
perLine,perWord :: (String -> String) -> (String -> String)
perLine f = onLines (map f)
perWord f = onWords (map f)Some examples:
string function frunIO (tv test0 f)idTo see a World in a Grain of Sand And a Heaven in a Wild Flower, Hold Infinity in the palm of your hand And Eternity in an hour. - William Blake
reverseekalB mailliW - .ruoh na ni ytinretE dnA dnah ruoy fo mlap eht ni ytinifnI dloH ,rewolF dliW a ni nevaeH a dnA dnaS fo niarG a ni dlroW a ees oT
onLines reverse- William Blake And Eternity in an hour. Hold Infinity in the palm of your hand And a Heaven in a Wild Flower, To see a World in a Grain of Sand
perLine reversednaS fo niarG a ni dlroW a ees oT ,rewolF dliW a ni nevaeH a dnA dnah ruoy fo mlap eht ni ytinifnI dloH .ruoh na ni ytinretE dnA ekalB mailliW -
perLine (perWord reverse)oT ees a dlroW ni a niarG fo dnaS dnA a nevaeH ni a dliW ,rewolF dloH ytinifnI ni eht mlap fo ruoy dnah dnA ytinretE ni na .ruoh - mailliW ekalB
There are more examples in the TV repository and in the in the GuiTV repository. See also "separating IO from logic -- example".