ThreadScope Tour/Profile
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Objectives
Examine a ThreadScope profile on a realistic program
Concepts
- HEC - Haskell Execution Context; basically there is one HEC for each core you enable with the RTS option -N
Steps
Build sudoku2 and view its eventlog in ThreadScope
rm sudoku2 ghc -O2 sudoku2.hs -threaded -rtsopts -eventlog ./sudoku2 sudoku17.1000.txt +RTS -N2 -ls threadscope sudoku2.eventlog
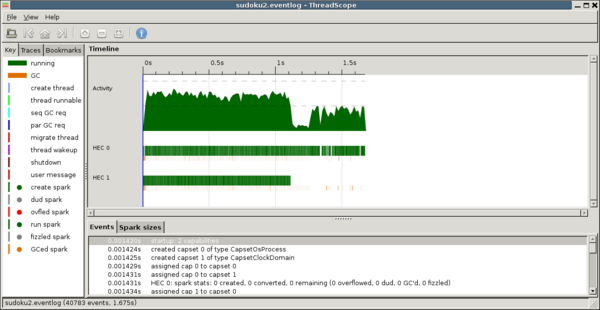
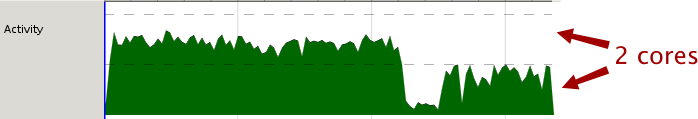
Examine the activity graph. The dashed horizontal lines provide hints about the amount of activity you might expect. Here for example we are using two cores, which is reflected the line dividing the graph into two pieces.
In the example above, we can see both cores nearly maxed out until around 1.85s at which point the amount of activity drops down to half.
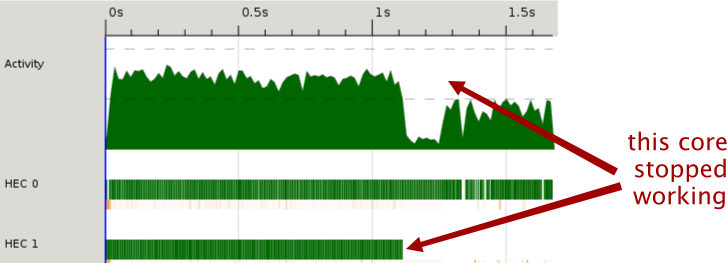
To see how this activity is distributed between cores, have a look at the HECs just below.
It so happens that the reason the activity dropped in half is that one of the cores stopped working.
Questions and exercises
- What do you think is causing the uneven division between the 2 cores?
- If you have more than 2 course available, what happened when you enable them?
- Try profiling the k-means example and studying the profile.